Article Contents ::
- 1 GOITER of THYROID
- 2 Types of GOITER
- 3 Causes of THYROIDITIS are
- 4 THYROIDITIS Clinical features
- 5 THYROIDITIS Diagnosis
- 6 SICK EUTHYROID SYNDROME
- 7 DIFFUSE NON-TOXIC SIMPLE GOITER
- 8 SIMPLE GOITER Clinical manifestations
- 9 SIMPLE GOITER Diagnosis
- 10 SIMPLE GOITER Treatment
- 11 NON-TOXIC MULTINODULAR GOITER
- 12 NON-TOXIC MULTINODULAR GOITER Treatment
- 13 TOXIC MULTINODULAR GOITER
- 14 TOXIC MULTINODULAR GOITER Treatment
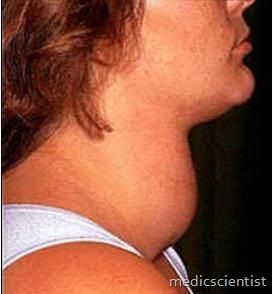
GOITER of THYROID
- Acute thyroiditis is an inflammatory condition of thyroid due to suppurative infection.
- enlarged thyroid gland may be caused by thyroiditis, benign thyroid nodules, malignancy, iodine deficiency,
- or any condition that causes hyperfunction or hypofunction of the gland
Types of GOITER
- aberrant goiter: A supernumerary goiter.
- acute goiter: A goiter that grows rapidly.
- adenomatous goiter: A goiter caused by the growth of an encapsulated adenoma.
- colloid goiter: A goiter in which there is a great increase of the follicular contents.
- congenital goiter: A goiter present at birth.
- cystic goiter: A goiter in which a cyst or cysts are formed, possibly resulting from the degeneration of tissue or
- liquefaction within an adenoma.
- diffuse goiter: A goiter in which the thyroid tissue is diffuse, in contrast to its nodular form as in adenomatous goiter.
- diving goiter: A movable goiter, located either below or above the sternal notch.
- endemic goiter: Goiter development in certain geographic localities, esp. where the iodine content in food and water is deficient. Goiters are more prevalent in fresh water and lake areas and less so on the seacoast, owing to the lack of iodine in fresh water. The treatment consists of iodine taken orally or in iodized salt.
- fibrous goiter: A goiter with a hyperplastic capsule.
- intrathoracic goiter: A goiter in which a portion of the thyroid tissue lies within the thoracic cavity.
- lingual goiter: A hypertrophied mass forming a tumor at the posterior portion of the dorsum of the tongue.
- nodular goiter: A goiter that contains nodules.
- parenchymatous goiter: A usually diffuse goiter characterized by multiplication of cells lining the follicles or alveoli. Colloid is usually reduced and the follicular cavities assume various sizes and are often obliterated by the infoldings of their walls. Fibrous tissue may increase markedly. The iodine content of the gland is low.
- perivascular goiter: A goiter surrounding a large blood vessel.
- retrovascular goiter: A goiter that develops behind a large blood vessel.
- simple goiter: A goiter unaccompanied by constitutional symptoms.
- substernal goiter: An enlargement of the lower part of the thyroid isthmus.
- suffocative goiter: A goiter that causes shortness of breath owing to pressure.
- toxic goiter: An exophthalmic goiter or a goiter in which there is an excessive production of the thyroid hormone.
- vascular goiter: A goiter due to distention of the blood vessels of the thyroid gland.
Causes of THYROIDITIS are
- · Bacterial infections
- · Staphylococcus
- · Streptococcus
- · Fungal infection
- · Rad iation thyroid itis
- · Amiodarone
- · Viral
- · Mycobacterial infection
- · Autoimmune – Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- · Riedel’s thyroiditis
- ·Parasitic thyroiditis.
THYROIDITIS Clinical features
- · Pain, fever
- · URTI
- · Sore throat
- · Tender goiter.
THYROIDITIS Diagnosis
- is by thyrotoxic features, hypothyroidism and recovery.
- Treatment is Aspirin 600 mg 6 hourly NSAIDs
- Glucocorticoids – Prednisone 60 mg tapered in 8 weeks
- For hypothyroidisM, levothyroxine may be given.
SICK EUTHYROID SYNDROME
- Any acute severe illness can cause disturbance of thyroid function without any underlying thyroid disease.
- Therefore thyroid function should be avoided in acutely ill patients.
DIFFUSE NON-TOXIC SIMPLE GOITER
- There is diffuse enlargement of thyroid but no nodules.
- There is no hyperthyroidism.
- It is also called colloid goiter or endemic goiter. It is found in iodine-deficient areas commonly. TSH is normal.
- It may be caused by goitrogens like cabbage, cauliflower etc.
SIMPLE GOITER Clinical manifestations
- Usually asymptomatic
- Goiter is diffuse, large, non tender, soft
- Substernal goiter may cause obstruction of thoracic inlet with faintness, facial congestion and external jugular vein obstruction when the arms are raised above the head. This is called Pemberton’s sign.
SIMPLE GOITER Diagnosis
- is by normal TSH,
- normal T3,
- low or normal T4
SIMPLE GOITER Treatment
- is Iodine or Thyroid hormone replacement.
- Levothyroxine is given 100 IJg/day so that TSH is lownormal.
- Surgery is done for big goiters.
NON-TOXIC MULTINODULAR GOITER
- It is common in women.
- Found in iodine-deficient regions due to multiple factors like genetic, autoimmune and environmental factors.
- Multinodular goiter causes enlargement in the neck with compressive symptoms, if large.
- Hoarseness may also occur due to compression of laryngeal nerve.
- It may be malignant.
NON-TOXIC MULTINODULAR GOITER Treatment
- consists of both symptomatic relief and decreasing the production of thyroid hormone
- is low dose levothyroxine, glucocorticoids, surgery.
TOXIC MULTINODULAR GOITER
- It is like non-toxic MNG (Multinodular goiture). There be mild thyrotoxicosis or subclinical hyperthyroidism.
- Age is elderly.
- There may be atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, nervousness, weight loss.
- TSH is low and T4may be increased.
- Thyroid scan shows increased uptake from multiple regions.
TOXIC MULTINODULAR GOITER Treatment
- is Antithyroid drugs, Beta blockers, radio-iodine, surgery.
