Home » Diseases & Diagnosis » Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar vector-borne disease by protozoa called Leishmania Diagnosis Treatment
Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar vector-borne disease by protozoa called Leishmania Diagnosis Treatment
all about Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar Diagnosis signs and symptoms
- with treatment and classification of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar
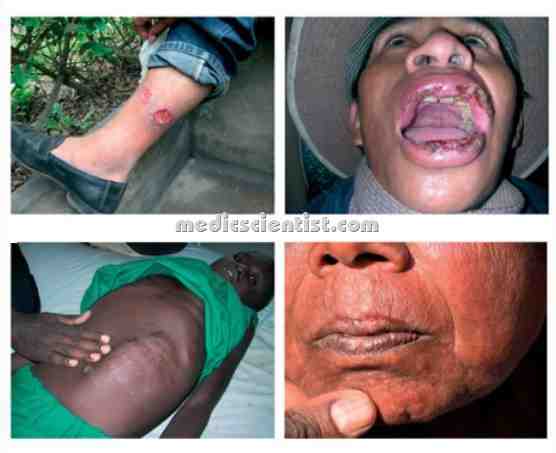 |
| Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar Diagnosis signs and symptoms with treatment |
- Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar is a disease caused by protozoa called Leishmania.
- Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar is a vector-borne disease.
- Rodents are reservoir hosts and humans are incidental hosts for Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar .
Types Classification of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar —
|
| Types Classification of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar Visceral Leishmaniasi |
|
| Types Classification of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar Visceral Leishmaniasi |
1. Visceral Leishmaniasis –
- due to infection of macrophages in reticuloendothelial system by Leishmania donovani.
|
| Classification of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar Cutaneous Leishmaniasis |
|
| Classification of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar Cutaneous Leishmaniasis |
2. Cutaneous Leishmaniasis –
- due to infection of macrophages in skin by Leishmania mexicana.
|
| Mucosal Leishmaniasis Classification of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar |
|
| Mucosal Leishmaniasis Classification of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar |
3. Mucosal Leishmaniasis
- due to infection of nasopharyngeal mucosa by Leishmania amazonensis.
Etiology of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar —
- Leishmaniasis is caused by Leishmania or Viannia.
|
| Leishmaniasis is caused by Leishmania or Viannia |
- The female sand fly (Phlebotomus) bites the host and injects promastigotes which enter the macrophages.
|
| The female sand fly (Phlebotomus) |
- They multiply, and when the macrophages rupture, amastigotes are liberated into the blood which are again ingested by sandflies.
- and the life cycle of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar will continue to next to next.
|
| life cycle of Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar |
Diagnosis of Leishmaniasis —
- The amastigotes can be seen under the microscope in a thin smear or histology section.
- Skin testing for delayed type hypersensitivity reactions are also useful.
Visceral Leishmaniasis —
- Visceral Leishmaniasis Occurs through bite of sandfly, by blood transfusion, or needle sharing. The disease may be acute, subacute or chronic.
- Incubation period of Visceral Leishmaniasis may be weeks, months or years. This disease is also called Kala-azar or Black fever as the patients appear grey.
- There is fever, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, peripheral lymphadenopathy. Spleen may be very big, soft and non-tender.
- There is pancytopenia – anaemia, leukopenia, lymphocytosis, monocytosis, thrombocytopenia, hypergammaglobulinaemia, hypoalbuminemia.
- Some patients may have dermal leishmaniasis in Kalaazar.
Diagnosis of Visceral Leishmaniasis —
- Parasites may be seen in peripheral smear, tissue aspirates, biopsy specimen of spleen, liver, bonemarrow or lymph node.
- Presence of Visceral Leishmaniasis is seen as a nucleus and a kinetoplast (extra nuclear DNA) called LD bodies, which is very typical of kala-azar.
- Patients of florid kala-azar have high titers of LD antibodies (Leishmanin or Montenegro test). ,
Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar Treatment —
- Pentavalent antimonial compound – 20 mgjkg daily for 28 days.
- Amphotericin B – 15 to 20 mgjkg daily.
- r;.-/ Paromom cin (amino I coside – 15 to 20 mgj kg daily for 21 days.
- Miltefosine – Dose 50-100 mg daily for 28 days. Visceral leishmaniasis is common in persons with HIV and need HAART (highly active antiretroviral therapy).
|
| Leishmaniasis or Kala-azar Cutaneous Leishmaniasis |
Cutaneous Leishmaniasis –
- incubation period is from weeks to months.
- There is a papule at the site of bite, and lymphadenopathy.
- There may be change of papule to nodule and ulcerative lesion with central depression and raised border several cms. in size.
- in Cutaneous Leishmaniasis Satellite lesions and secondary bacterial infection may occur.
Treatment Cutaneous Leishmaniasis —
- Amphotericin B
- Miltefosine
Mucosal Leishmaniasis —
- Mucosal Leishmaniasis Nasopharyngeal mucosa is infected and is quite disfiguring.
- Mucosal Leishmaniasis is caused by Viannia. There are persistent nasal symptoms, and epistaxis.
Treatment of Mucosal Leishmaniasis —
- Amphotericin,
- Antimonial compounds
- and glucocorticoids.


