Article Contents ::
- 1 INSULIN RESISTANCE SYNDROMES or Syndrome X Overview
- 2 (metabolic syndrome)- consists of :
- 3 Current ATP III criteria define the metabolic syndrome as the presence of any three of the following five traits:
- 4 Severe insulin resistance is due to:
- 5 Prevention of Type 2 DM
- 6 Criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
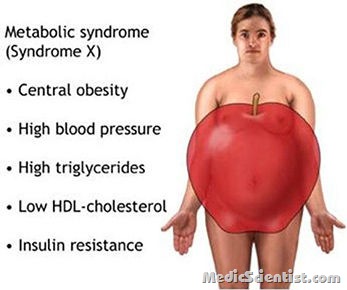
INSULIN RESISTANCE SYNDROMES or Syndrome X Overview
(metabolic syndrome)- consists of :
Insulin resistance Hypertension Dyslipidemias Obesity – central Endothelial dysfunction Accelerated cardiovascular disease. The co-occurrence of metabolic risk factors for both type 2 diabetes and CVD (abdominal obesity, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemias, and hypertension) suggested the existence of a “metabolic syndrome” . A similar profile can be seen in individuals with abdominal obesity who do not have an excess of total body weight Other names applied to this constellation of findings have included syndrome X,
Current ATP III criteria define the metabolic syndrome as the presence of any three of the following five traits:
- Blood pressure ≥ 130/85 mmHg or drug treatment for elevated blood pressure
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥ 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) or drug treatment for elevated blood glucose
- Abdominal obesity, defined as a waist circumference in men >102 cm (40 in) and in women >88 cm (35 in)
- Serum triglycerides ≥ 150 mg/dL (1.7 mmol/L) or drug treatment for elevated triglycerides
- Serum HDL cholesterol <40 mg/dL (1 mmol/L) in men and <50 mg/dL (1.3 mmol/L) in women or drug treatment for low HDL-
Severe insulin resistance is due to:
- Type A – disorders of insulin signal pathway.
- Type B – insulin receptor auto-antibodies.
- Type A
-
- Young women
- Severe hyperinsulinemia Obesity
- Hyperandrogenism
- Defect in insulin signaling pathway
- Type B
-
- Middle aged women
- Severe hyperinsulinemia
- Hyperandrogenism
- Auto immune disorder antibodies against insulin receptors
Acanthosis nigricans
- · Acanthosis
- · Hyperandrogenism – Hirsutism
- – Acne
- – Oligomenorrhoea.
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
- · Affects premenopausal women
- · Chronic anovulation
- · Hyperandrogenism
- · Insulin resistance
- · Type 2 DM
- ·Obesity. /treatment Metformin
- Thiazolidinediones.
Prevention of Type 2 DM
- Life style modifications –
- · Diet
- · Exercise (30 min/day) for 5 days a week
- · Weight reduction.
- Metformin (to reduce blood sugar and weigt)
- Thiazolidinediones
- Ramipril
- Pravastatin (lipid powering).
Criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
- Symptoms of diabetes and a casual plasma glucose 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/l). Casual is defined as any time of day without regard to time since last meal.
- The classic symptoms of diabetes include polyuria, polydipsia, and unexplained weight loss. or
- FPG 126 mg/dl (7.0 mmol/l). Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 hours. or
- 2-h(Hour) plasma glucose 200mg/dl (11.1 mmol/l) during an OGTT. The test should be performed as described by the World Health Organization, using a glucose load containing the equivalent of 75 g anhydrous glucose dissolved in water.