Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis Signs and Symptoms CARDIOMYOPATHY
- Causes Etiology Types Diagnosis of Cardiomyopathy with Treatment Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathies are a group of diseases which involve the heart muscles and affect cardiac functions. Any disease that affects the heart muscle, diminishing cardiac performance There is primary involvement of heart muscles. There is no evidence of any heart disease like hypertension, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, coronary artery disease, or pericardial disease.
- Primary cardiomyopathies, which may be genetic, mixed (genetic or non genetic), or acquired,
- The heart muscle disease or caradiomyopathy resulting from chronic ischemia is called ischemic cardiomyopathy.
- secondary cardiomyopathies, which are accompanied by other organ system involvement.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
- Unclassified cardiomyopathies
Cardiomyopathy RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHY Causes Etiology Types Diagnosis of Cardiomyopathy with Treatment Cardiomyopathy
- Cardiomyopathy is primary disease of the heart muscles.
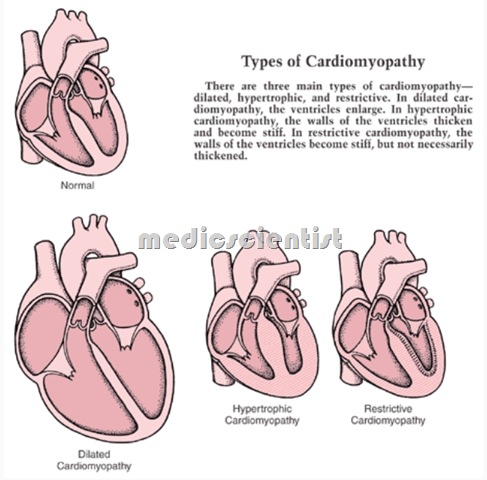
Cardiomyopathy is of three types:
- Dilated caradiomyopathy
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy.
Etiology of Cardiomyopathy
- 1. Idiopathic
- 2. Familial
- 3. Eosinophilic restrictive cardiomyopathy
- 4. Endomyocardial fibrosis
- 5. Infective causes:
- a.Viral e. Metazoal
- b.Bacterial f. Spirochetal
- c.Fungal g. Rickettsial
- d. Protozoal
- 6. Metabolic
- 7. Deficiency
- 8. SLE
- 9. Polyarteritis nodosa
- 10. Rheumatoid arthritis
- 11. Progressive systemic sclerosis
- 12. Amyloidosis
- 13. Sarcoidosis
- 14. Muscular dystrophy
- 15. Friedreich’s ataxia
- 16. Alcoholic
- 17. Radiation
- 18. Drugs
- 19. Peripartum cardiomyopathy.
Cardiomyopathy RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHY Causes Etiology Types Diagnosis of Cardiomyopathy with Treatment Cardiomyopathy
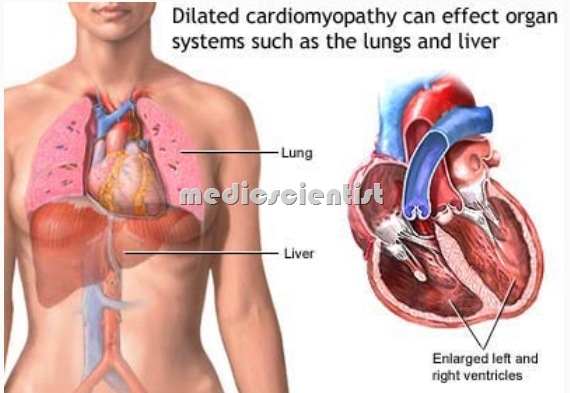
DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY (DCMP)
- There is dilatation of the left and / or right ventricles. Ventricular systolic Pump functionis impaired. There isprogressive increase in heate size.
- The Ventricular wall becomes thinned out this process is called remodeling . –
Cardiomyopathy Etiology:
- Etiology is:
- Toxic, metabolic, infectious.
- Viral myocarditis is a common cause of OeM!!..
DCMP is common in
- Middle aged men
- Alcohol abuse
- Pregnancy
- Thyroid disease
- Cocaine abuse
- Chronic tachycardias.
- Geneticall it may be autosomal recessive X-linked inheritance. ‘
Cardiomyopathy Clinical features: symptoms :
- Chest pain,
- dypnoea fatigue,
- palpitations syncopes
- stemic embolism
Signs: –
- LV dilatation
- Signs of CHF
- Narrow pulse pressure
- Raised JVP
- S3, S4
- MR, TR.
Cardiomyopathy Diagnosis:
Cardiomyopathy RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHY Causes Etiology Types Diagnosis of Cardiomyopathy with Treatment Cardiomyopathy
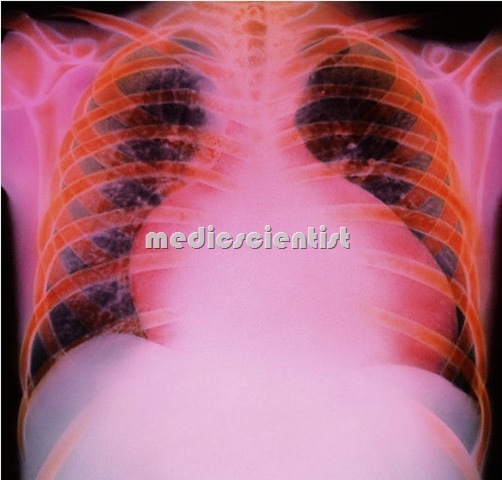
Cardiomyopathy Chest x-ray may show
- – Cardiomegaly
- – LV dilatation
- – Pulmonary hypertension
- – Interstitial edema
Cardiomyopathy RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHY Causes Etiology Types Diagnosis of Cardiomyopathy with Treatment Cardiomyopathy
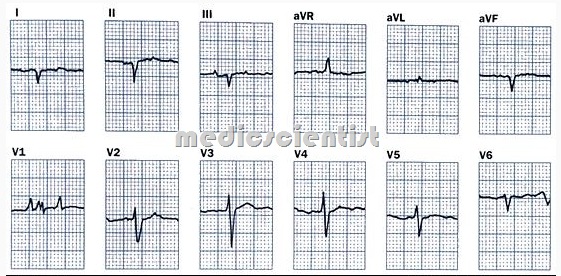
Cardiomyopathy ECG may show –
- Sinus tachycardia
- Atrial fibrillation
- Ventricular arrhythmias
- Left atrial enlargement
- ST-T changes
- Conduction defects
- Low voltage ECG
Cardiomyopathy RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHY Causes Etiology Types Diagnosis of Cardiomyopathy with Treatment Cardiomyopathy
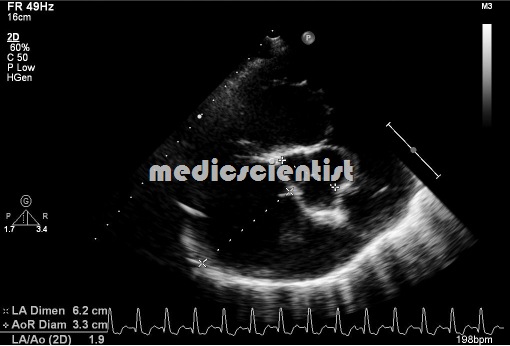
Cardiomyopathy Echocardiography :
- – LV dilatation
- – Systolic dysfunction
- – Reduced ejection fraction.
BNP:
- – Brain natriuretic peptide is elevated.
Cardiac catheterization: for-
- – Angiography
- – LV, and coronary
- – MR seen
- – Ejection fraction is measured
- – Transvenous endomyocardial biopsy.
Cardiomyopathy Treatment
- A majority die within 3 yrs of symptoms
- Salt restriction
- ACE inhibitors
- Digitalis
- Diuretics
- Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) Spirinolactone
- Beta blockers
- Stop alcohol and cardiotoxic drugs Stop NSAIDs
- Biventricular pacing or CRT – cardiac resynchronization therapy
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator
- Cardiac transplantation.
- Stem cell therapy
Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy
- Alcohol is cardiotoxic and ma cause heart failure or fatal ventricular tachyarrh thmias.
- Holiday Heart Syndrome – After a bout of heavy drinkinging, atria fibrilation Or VPCs are seen. –
Peripartum Cardiomyopathy
- ardiac dilatation and heart failure occurs from 3 months before deliver to 6months after delivery. ommon in multipara. Age usually more than-3D
There is DCMP.
- There is progressive increase in heart size with each pregnancy.
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY
- There is left ventricular hypertrophy without known cause.
- LV is not dilated .
- There is asymmetric LVH and h ertrophy ..Qf int~rventricuar septum.
- There is dynamic LV outflow obstruction (obstruction during contraction of the heart). –
- Dynamic LV obstruction is due to hypertrophy of outflow tract which reduces the outflow from left ventricle during midsystole.
- There is systolic anterior motion of the anterior mitral leaflet. It is also called Idio atbic Hypertrophie Subaortic Stenosis IHSS . –
- there is diastolic dysfunction.
Clinical features
- · There may be mild symptoms
- · However, sudden death can occur.
- · Dyspnoea, angina, fatigue, syncope may occur
- · There may be double or triple apical cardiac im-
pulse
- · Rapid carotid upstroke
- · S4
- · There is a harsh, diamond-shaped murmur after the fi rst hea rt sou nd.
Diagnosis ECG:
- Dee waves in Vl & V2
- Atrial and ventricular arrhythmias
Chest x-ray:
- – May be normal.
Echocardiography:
- – LVH
- Septum 1.3 times the thickness of posterior
- LV free wall
- S stolic AntruQ otion (SAf1) of mitral valv~
- LV cavity is small in HOCM.
Treatment
- Beta blockers
- Prevent dehydration
- Amiodarone, and Disopyramide for ventricular arrrhythmias
- Verapamil, Diltiazem
- Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT)
- Injection of ethanol in interventricular septum to shrink it
- Septal myectomy
- Implantable cardioverter defibrillator. ~Digitalis, diuretics, nitrates, vasodilators, are not used.
RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHY
- Restrictive Cardiomyopahty is characterized by abnormal diastolic function. The ventricular walls are rigid a-nd revent proper filling. – —
Etiology :-
- Amyloid infiltration
- Glycogen
- Hemochromatosis
- Endomyocardial fibrosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Scleroderma
- Eosinophilia.
CIinical features
- — Dyspnoea
- — Pedal edema
- — Tender liver
- — Kussmaul’s sign – JVP is raised during inspiration
- — Distant heart sounds (soft, faint heart sounds)
- S3,S4
- MR.
ECG
- ST-T changes,
- arrhythmias
Echocaradiography:
- Symmetrical, thickened LV walls
- Decreased cardiac output, decreased ejection fraction
- Increased End diastolic pressure (EDP).
- It can be differentiated from constrictive pericarditis by a palpable apex beat and mitral regurgitation.
ENDOMYOCARDIAL FIBROSIS
- Common in Africa.
- · There is restrictive cardiomyopathy
- · There are fibrous endocardial changes in AV valves (mitral valve, tricuspid valves)
- · There is MR, TR
- There is apical fibrosis
- Treatment is surgical excision of fibrotic endocardium.
EOSINOPHILIC ENDOMYOCARDIAL DISEASE
- Also called Loeffler’s endocarditis.
- There is hypereosinophilic syndrom~.
- · Endocardium of RV and LV is thickened.
- There is restrictive cardiomyopathy.
- · There are large thrombi in venericles with embolization.
- Liver and spleen are enlarged.
- There is eosinophilic infiltrati~ of many organs. Treatment is diuretics anticoa ulation glucocorticoids, hydroxyurea.
RIGHT VENTRICULAR DYSPLASIA
- Familial cardiomyopathy resembling dilated car-iomyopathy.
- Right ventricular wall is re laced b adi ose tis~.
- Ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death may occur.
- · Implantable cardioverter defibrillator is implanted.
NEUROMUSCULAR DISEASE WITH CARDIAC INVOLVEMENT
- · Duchenne’s progressive muscular dystrophy, myotonic dystrophy, Friedreich’s ataxia may show hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM) or dilated cardiomyopathy (DCMP).
- Death often occurs due to ventricular arrhythmias.
DRUGS AND CARDIOMYOPATHY
- nthracycline derivatives
- Adriamycin
- yclophosphamide
- Cocaine.

