Acute Myocardial Infarction AMI Causes PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Atherosclerosis and Etiology
- Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) may present as unstable angina (no ST segment elevation), or acute myocardial infarction. Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) implies irreversible damage to the myocardium.
- MI Causes usually occurs when an atheromatous plaque in a coronary artery ruptures, and the resulting clot obstructs the injured blood vessel

Causes Acute Myocardial Infarction Etiology:
- Proven risk factors for MI are tobacco use,
- high blood pressure, male sex, advanced age, obesity, physical inactivity
- diabetes mellitus, abnormal cholesterol levels,
- high blood pressure, male sex, advanced age, obesity, physical inactivity
- AMI may be associated with ST elevation or ST depression in the ECG.
- AMI With ST elevation is called STEMI (ST segment elevation MI) and AMI without ST segment elevation is called NSTEMI (Non ST segi]1ent elevation MI).
- In NSTEMI cardiac markers like troponins are normal (not elevated).
- In TEMI~ardc markers like troponins are elevated.
- Q waves do not evolve in NSTEMI but Q waves are
- seen to evolve in STEMI. ~
- Mortalit is 30%. 25% die in 1st year after AMI
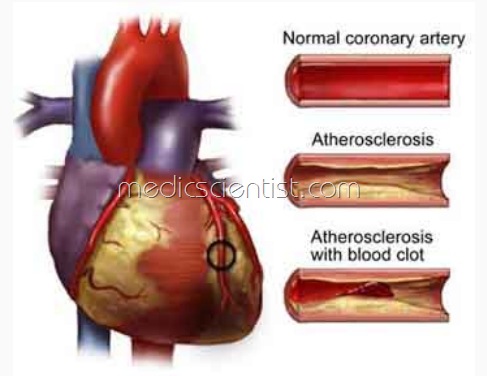
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Causes of Acute Myocardial Infarction
I. Atherosclerosis
- Coronary arteries are narrowed by atherosclerosis.
- Abrupt closure can occur by thrombotic occlusion.
- Very gradual narrowing leads to development of collaterals and therefore lesser incidence of MI.
Factors which precipitate thrombotic occlusion of coronary vessels are:
- Vascular injury (damage to endothelium of coronaries)
- Vascular injury is precipitated by cigarette smoking, hypertension and hyperlipidemia.
- Fissuring of atherosclerotic plaque
- Rupture of atherosclerotic plaque
- Ulceration
Acute Myocardial Infarction Causes Thrombogenesis
- Atherosclerotic plaque with rich lipid core and thin @:>rous cap are very p..!:one to rupture.
- Iatelets are activated by: ADP
- Collagen Epinephrine Serotonin.
- There is release of thromboxane A2•
Thtrhromboxane A2 is a potent
- vasoconstrictor which causes coronary spasm and precipitates total coronary oc~sion and infarctio’!.
- activated platelets are resistant to thrombolysis.
- Platelets also bring about a change in GP IIb / IIIa
- receptors which can now bind to 2 platelets at a time involving von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen.
- Prothrombin is converted to thrombin and fibrinogen to fibrin resulting in formation of clots.
II. Total Coronary occlusion resulting in Acute MI occurs due to :
- Presence of multiple risk factors
- Hypercoagulability
- Collagen vascular disease
- Cocaine abuse
- Intracardiac thrombi or masses leading to coronary embolization.
III. Other causes of Coronary occlusion are less important e.g. :
- Coronary embolism
- Congenital abnormalities
- Coronary spasm
- Systemic and inflammatory disease .
