Article Contents ::
- 1 AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) Transmission of HIV Clinical features and Course of HIV infection
- 2 AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
- 3 Persons at increased risk of HIV infection
- 4 Transmission of HIV infection
- 5 Body fluids which transmit HIV infection
- 6 Clinical features and Course of HIV infection Primary HIV
- 7 Opportunistic infections in HIV
- 8 Investigations HIV infection
- 9 Indications for HIV screening
- 10 Treatment HIV infection
- 11 HIV IN WOMEN
- 12 OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE
- 13 POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS
- 14 HIV AND TUBERCULOSIS
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) Transmission of HIV Clinical features and Course of HIV infection
AIDS is an advanced stage of HIV infection with symptoms and opportunistic infections, with the CD4 cell count below 200 cells / IJL. Most AIDS patients are typical progressors and have a median survival time of 10 years. Some AIDS patients may have no symptoms for up to 7 years.
 |
| AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) |
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
- It was first reported in 1981 in US and is now a worldwide epidemic. It is caused by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
- The HIV attacks the immune system of the body leading to a multitude of serious infections and cancers.
- An HIV positive individual is a patient who is infected with HIV but is asymptomatic.
- AIDS is an advanced stage of HIV infection with symptoms and opportunistic infections, with the CD4 cell count below 200 cells / IJL.
- Most AIDS patients are typical progressors and have a median survival time of 10 years. Some AIDS patients may have no symptoms for up to 7 years.
- Antiretroviral therapy has reduced the morbidity and mortality of HIV infection.
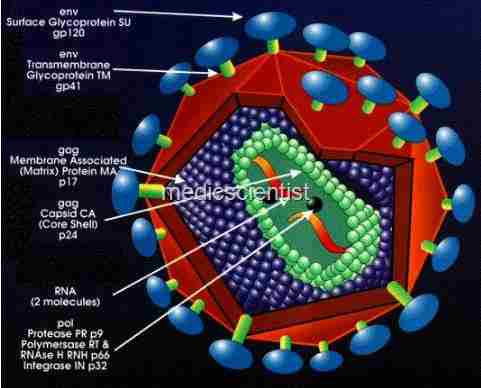 |
| human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) |
 |
| Persons at increased risk of HIV infection |
Persons at increased risk of HIV infection
- · Injection drug users
- · Recipients of blood products
- · People with multiple sex partners
- · Patients of sexually transmitted diseases
- · Commercial sex workers and their partners
- · Gay men – People who have sex with persons of same sex
- · Sexual partners of persons with AIDS
- · Travelers, who visit areas of increased prevalence and are indiscrete
- · Health care workers.
 |
| Transmission of HIV |
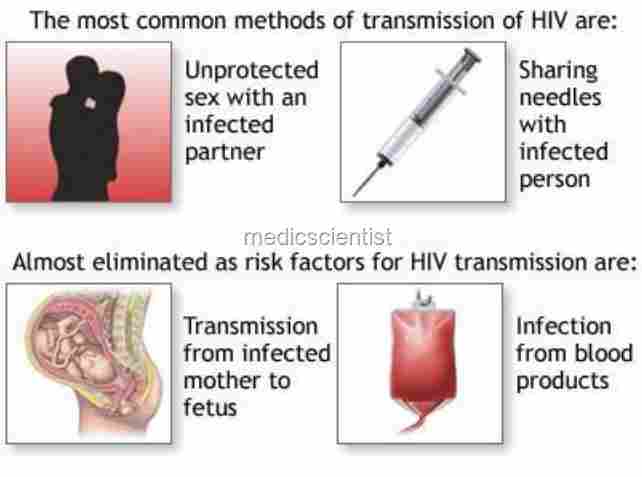
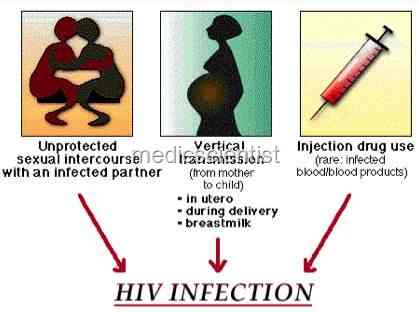
Transmission of HIV infection
- 1. Sexual contact.
- 2. Transfusion of infected blood and blood products.
- 3. Mother to child – HIV is transmitted from infected mother to child during pregnancy, during delivery, or after birth through breast- feeding.
- 4. Contact with infected instruments and body fluids – needle-sharing among drug users, acupuncture, tattooing, occupational exposure, medical procedures, contact with body fluids.
- Insects which feed on human blood cannot spread HIV.
Body fluids which transmit HIV infection
- · Semen
- · Vaginal secretions
- · Cerebrospinal fluid
- · Pleural fluid
- · Peritoneal fluid
- · Pericardial fluid
- · Amniotic fluid.
 |
| Clinical features and Course of HIV infectionPrimary HIV |
Clinical features and Course of HIV infection Primary HIV
- There are non-specific, flu-like symptoms.
- Fever
- Lethargy
- Sore throat
- Malaise
- Rash Lymphadenopathy Arthralgias
- Myalgias Headache-Men i ng itis.
- Symptoms occur within 2 to 6 weeks after virus enters the body. Symptoms usually resolve in 2 to 3 weeks.
 |
| Clinical features and Course of HIV infectionPrimary HIV |
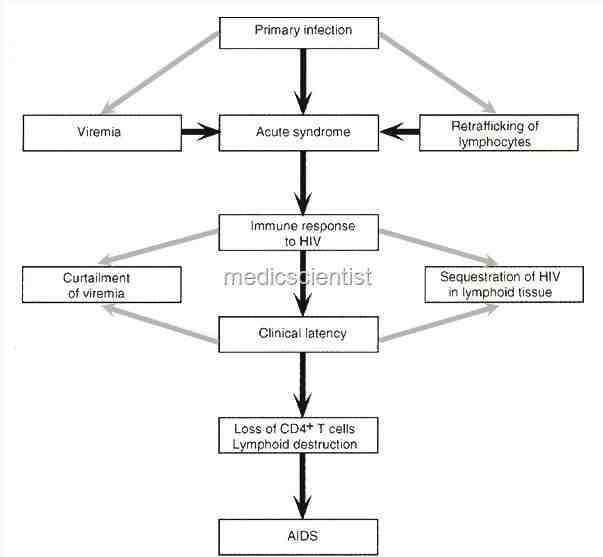
From 2 to 6 weeks the person is very infectious and the virus is present in large quantities in genital fluids.
- Severe symptoms occur after 10 years or more in adults.
- The virus multiplies and kills the cells of the immune system especially CD4 T lymphocytes resulting in a decreasing number of CD4 cells.
- There is immunodeficiency and increased susceptibility to opportunistic infections and cancers.
- HIV infects the CNS, testes and other organs.
The virus remains latent in CD4 cells, hence it is not possible to eradicate HIV.
As immune function deteriorates, death becomes certain.
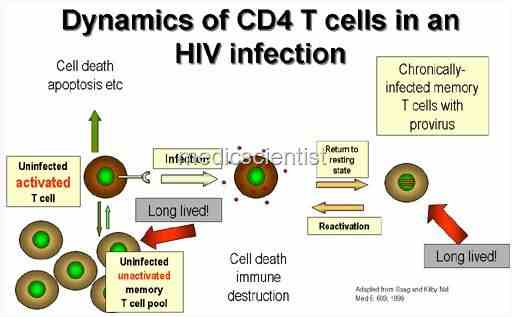 |
| HIV virus remains latent in CD4 cell |
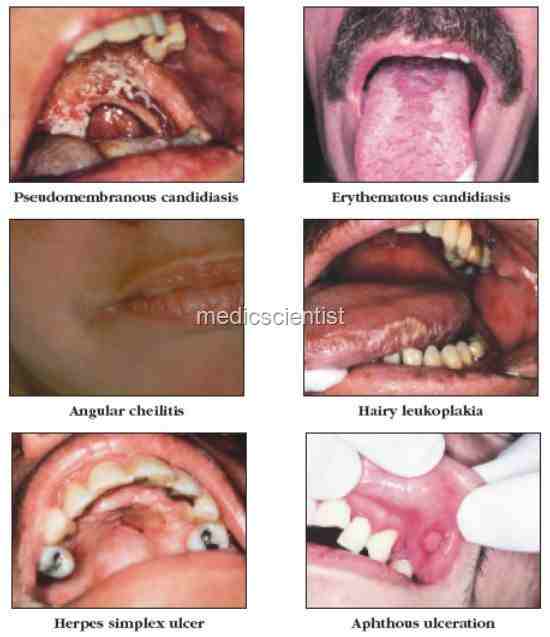
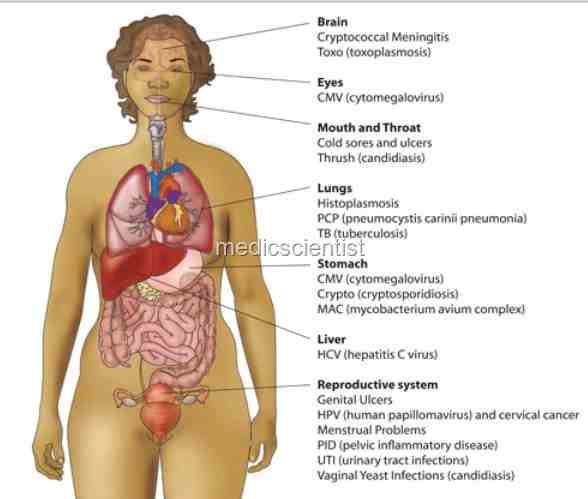
Opportunistic infections in HIV
- · Tuberculosis
- · Oropharyngeal candidiasis
- · Diarrhoea due to :
- Salmonella Shigella – Campylobacter
- – Clostridium difficile
- – Giardia
- – Amoeba
- – Isospora belli
- · Strongyloides
- · Cytomegalovirus
- – Herpes simplex j Varicella zoster virus
- – Bacterial pneumonia
- – Cryptococcal meningitis
- – Toxoplasmosis
- – Pneumonia due to Pneumocystis carinii
- – Mycobacterium avium complex infections
- – Cytomegalovirus retinitis
- – Kaposi’s sarcoma
- – Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
 |
| Opportunistic infections in HIV |
 |
| hiv Investigations |
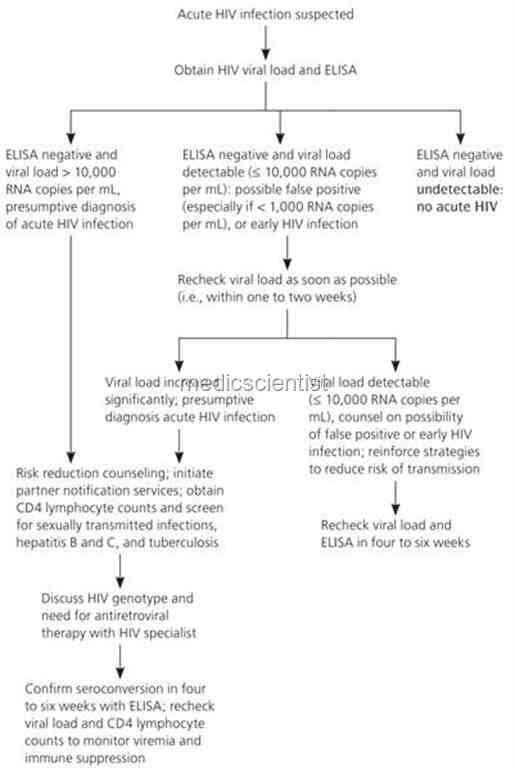
Investigations HIV infection
- · ELISA +ve test is found within 3 months of getting the infection.
- · HIV infection is diagnosed on the basis of 3 ELISA tests.
- · AIDS is diagnosed on the basis of 2 ELISA rapid tests using different antigens.
- · Western Blot is used for confirmation of indeterminate ELISA results.
- · Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays – Presence of HIV DNA is diagnostic.
- · Rapid oral HIV test.
 |
| Indications for HIV screening |
Indications for HIV screening
- · All individuals at high risk
- · Pregnant women
- · Donors of blood, semen, organs
- · All hospitalized patients where HIV prevalence
- rate is more than 1 per 1000
- · Patients of STD (sexually transmitted diseases)
- · Recurrent genital infections
- · Generalized lymphadenopathy
- · Recurrent herpes simplex or zoster
- · Tuberculosis
- · Unexplained weight loss or fever
- · Chronic diarrhea and Encephalopathy
- · Opportunistic infections.
Treatment HIV infection
- Antiretrovirals – these inhibit the viral replication
- Treatment of opportunistic infections Psychosocial support. Antiretroviral therapy:
- Antiretroviral therapy should be started when CD4 count goes below 350 to 200 cells jlJL or HIV RNA is above 55,000 copiesjml.
- If CD4 counts are not available, total lymphocyte count may be used.
- All symptomatic patients must be given antiretroviral therapy.
- Antiretroviral therapy must be continued indefinitely, with regular monitoring.
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) :
- HAART is a triple or 4 drug antiretroviral regime to suppress HIV replication for a long time.
- This leads to increased CD4 count and reduction in HIV RNA.
 |
| HIV IN WOMEN |
HIV IN WOMEN
- Maternal HIV transmission can occur to the fetus during labour and delivery or after birth via breast feeding.
- HIV transmission is common during late pregnancy, labour and delivery.
- Maternal transmission of HIV occurs if there is low CD4 count, first-born twins, high viral loads.
OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE
- Nurses, lab technicians, doctors, residents, paramedicals, medical students are at increased risk.
- Pricks on the skin can result in AIDS more than mucous membrane exposure.
- Direct contact with blood and body fluids during surgery or diagnostic procedures must be avoided.
POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS
- PEP means treatment of a person after exposure, with antiretroviral therapy.
- PEP should be started within 1-2 hours of exposure
- to prevent HIV infection. –
- – It should be started as early as possible after exposure.
- PEP consists of 28 days of :
- IZidovudine 300 mg BD + Lamivudine 150 mg BD OR
- tavudine 30 mg BD + Lamivudine 150 mg BD
- An expanded regimen consists of Indinavir 800 mg 8 hrly added to the above regime.
 |
| HIV AND TUBERCULOSIS |
HIV AND TUBERCULOSIS
- AIDS patients are very prone to tuberculosis especially MDR TB – Multidrug resistant tuberculosis. There is drug interaction between antiretrovirals and Rifampicin, hence special regimens have been devised.
Other infections
- Infections with Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter and even atypical and low virulence pathogens are very common in AIDS patients.
Other measures for longer life in HIV patients
- · Regular health checkup and monitoring
- · Avoid uncooked food
- · Use filtered water only
- · Well-balanced diet
- · Regular exercises
- · Personal hygiene
- · Avoid pets
- · Quit smoking, alcohol, drugs
- · Avoid stress
- · Plenty of sleep and rest.
