Article Contents ::
Antiplatelet, Anticoagulant & Fibrinolytic Therapy
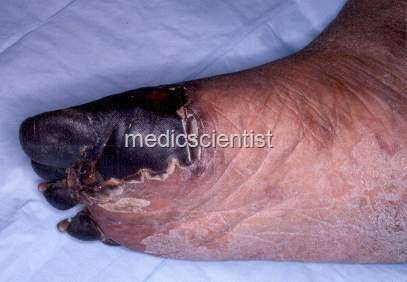 |
| venous thrombosis |
ANTIPLATELET, ANTICOAGULANT AND FIBRINOLYTIC THERAPY
- Arterial and venous thrombosis with embolic phenomenon like deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism and other embolizations result in morbidity and death.
Drugs which prevent thromboembolic phenomenon are:
 |
| Drugs which prevent thromboembolic phenom enon |
- 1. Drugs which inhibit platelet aggregation
- 2. Drugs which inhibit thrombin and fibrin generation.
ANTIPLATELET DRUGS
- These affect cyclooxygenase (COX), adenosine diphosphate receptors, platelet adhesions, glycoprotein (Gp), and thrombin.
- Gp lIb j IIIa on platelet surface is the final common pathway for platelet activation. Therefore, inhibiting this results in anticoagulation.
Aspirin
- It causes COX inhibition and prevention of thromboxane A2 synthesis, leading to decreased platelet activation and aggregation. The effect of aspirin occurs within 1 hour and lasts for 1 week. Dose is 75-325 mgjday.
Thienopyridines
- Ticlopidine and Clopidogrel inhibit ADP-induced platelet aggregation.
- The CAPRIE trial on these drugs demonstrated reduction in ischemic events in patients with MI and peripheral arterial disease.
Gp lIb / IlIa antagonists
- These are disintegrins which suppress fibrinogen e.g. Abciximab, Tirofiban.
- They are widely used in coronary artery disease.
ANTICOAGULANT DRUGS Heparin
- Unfractionated heparin (UFH) molecules bind to antithrombin potentiating its action and inactivating factor Xa and thrombin.
- This prevents and treats thrombosis in patients. Unfractionated heparin can be given IV or subcutaneously.
- It requires monitoring of aPTI – activated partial thromboplastin time.
- Antidote is protamine sulphate.
Low molecular weight heparin
- These are derived from cleavage of unfractionated heparin into low molecular weight compounds.
- They have more of anti-factor Xa but less of antithrombin activity.
- They are safer for use in patients of unstable angina, MI (myocardial infarction), DVT(deep vein thrombosis). Lab monitoring is not required.
- Examples are dalteparin, enoxaparin etc.
Heparinoids
- Act as anticoagulant by activating heparin co-factor – II. Only used if heparin causes thrombocytopenia.
Pentasaccharides
- Once weekly dose may be given for primary or secondary prevention of thromboembolic phenomenon.
Direct thrombin inhibitors
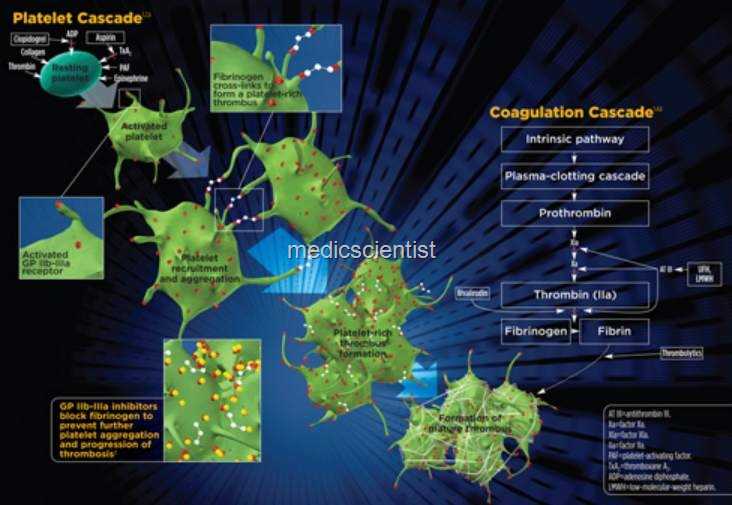 |
| Direct thrombin inhibitors |
Argatroban, LepirudinWarfarin
- It inhibits vitamin K reductase and prothrombin. It is not used in pregnancy.
- During Warfarin therapy PT – prothrombin time and INR are measured.
- INR of 2-3 is recommended.
- In prosthetic valves INR of 2.5 to 3.5 is recommended. INR is patients PT( prothrombin time) divided by the mean PT.
FIBRINOLYTIC DRUGS STREPTOKINESE
- This is obtained from beta hemolytic streptococci cultures.
- It is antigenic and can even cause anaphylaxis.
- It is used in MI and DVT (deep vein thrombosis) to lyse the clots.
UROKINASE
- It is obtained from human fetal kidney cell cultures or recombinant urokinase from mammalian tissue cultures.
- Tissue type plasminogen activator (RTPA) Recombinant tissue type plasminogen activator is used to treat DVT, pulmonary embolism, acute MI and acute strokes.
Indications for Anticoagulation
- That’s the short description about thrombosis, anticoagulant treatment, etc.· DVT – antocoagulants for 6 wks to 6 months
- · Pulmonary embolism – 6 months
- · Prosthetic heart valves – lifelong
- · MI – for variable duration
