Fungal Infections Superficial fungal infections and Systemic fungal infections
Superficial fungal infections are caused by
- numerousfungi that are capable of superficially invadingthe following:
- ▪ Skin , Nail apparatus▪ ,Mucosal sites, Oropharynx•
- Hair/hair follicles, Anogenitalia, Epidermis,
- These fungi are commensural organisms thatfrequently colonize normal epithelium.
- • Dermatophytes, Candida species, Malassezia species,
- Infections can extend more deeply in the immunocompromisedhost.
- Deeper, chronic cutaneous fungal infections canoccur after cutaneous inoculation.
- ▪ Mycetoma, Chromomycosis, Sporotrichosis
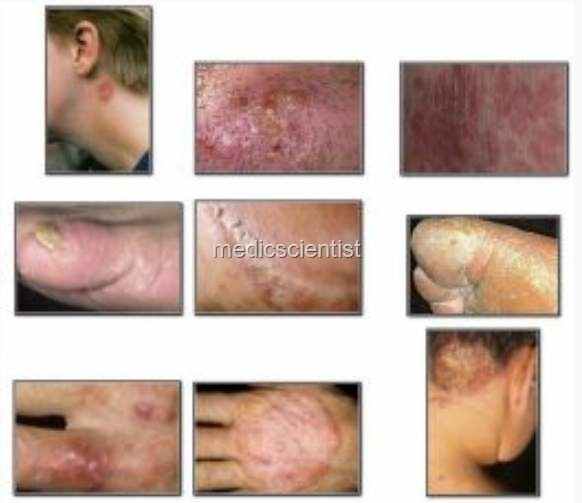 |
| Fungal Infections |
Systemic fungal infections with cutaneous dissemination;
- these infections occur most often inthe immunocompromised host.
- ▪ Primary lung infection; can disseminate hematogenouslyto multiple organ systems, includingthe skin
- Histoplasmosis.•
- Cryptococcosis
- • North American blastomycosis
- • Coccidioidomycosis
- Disseminated candidiasis commonly arises inthe GI tract.
- • Penicillinosis
- ▪ Primary gastrointestinal (GI) infection; neutropenichost
Etiology —
- Three genera of dermatophytes:
- Trichophyton
- M icrosporum
- E pidermophyton .
- • More than 40 species are currently recognized;approximately 10 spp. are commoncauses of human infection.
- • T. rubrum is the most common cause of epidermaldermatophytosis and onychomycosisin industrialized nations.
Under the microscope the fungi appear as rounded or budding forms or hyphae.
- The budding forms are like yeast (round or oval buds).
- The hyphae are molds( elongated rods).
- Yeast-like fungi are Candida and Cryptococcus.
- The mold like fungi are Aspergillus, Rhizopus, Ring worm fungi.
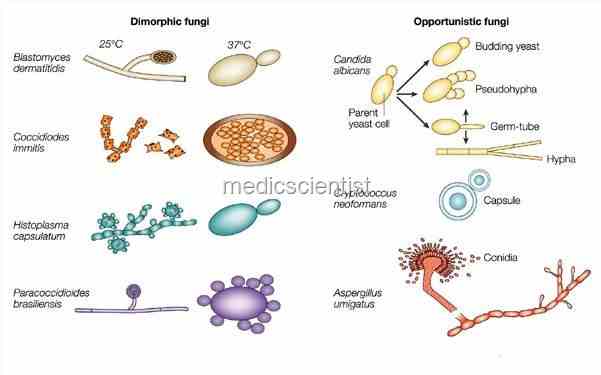 |
| Fungal Infections Dimorphic fungi |
Fungal Infections Dimorphic fungi (have 2 forms) – are
- histoplasmosis,
- blastomycosis,
- sporotrichosis,
- coccidiodomycosis.
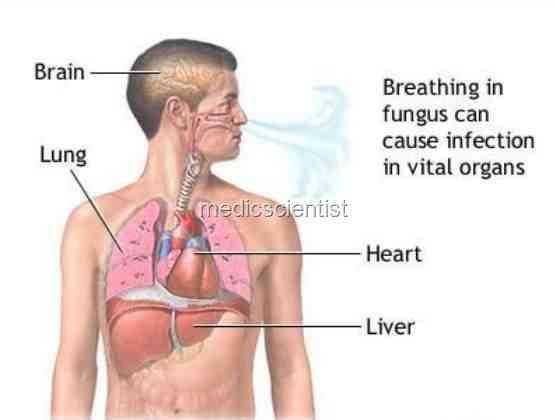 |
| Fungal Infections coccidiodomycosis |
- They are spherical but grow like molds (hyphae).
- Candida grows like budding yeast called pseudo hyphae.
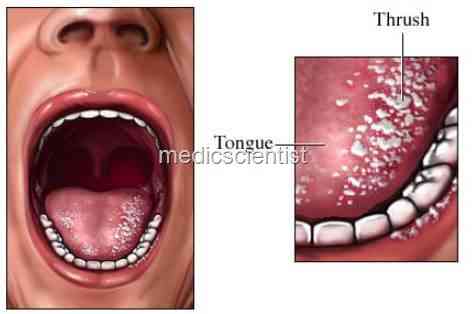 |
| Fungal Infections Candida grows |
- Pneumocystis are also fungi.
- Ring worm, Pityriasis versicolor, and Piedra infect the skin and its appendages.
- Deep mycoses occurs by inhalation.
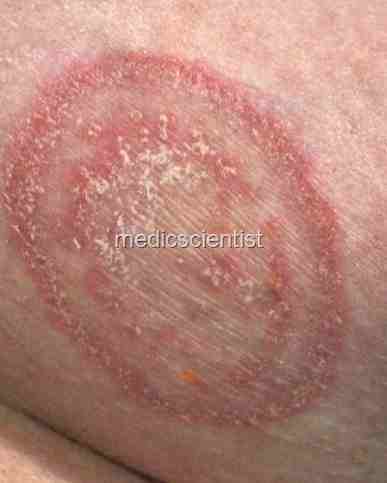 |
| Fungal Infections Ring worm, Pityriasis versicolor |
- Candida albicans is a normal commensal in the mouth but when the mucosa or skin is breached by disease, or surgery, or trauma, then infection occurs.
- Aspergillus and Fusarium infect the host when immunologically compromised.
Diagnosis Fungal Infections
- · Microscopic examination of smears or biopsy specimen.
- · Fluorescence microscopy with calcofluor staining is a sensitive technique for sputum, bronchial lavage fluid, and pus.
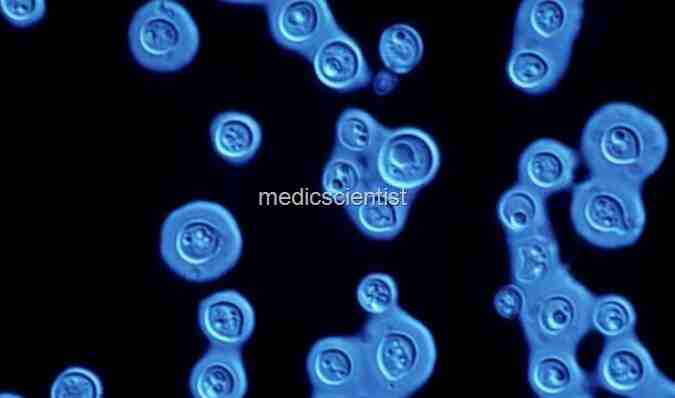 |
| India ink smear is used to detect Fungal Infections cryptococci in CSF |
- · India ink smear is used to detect cryptococci in CSF.
- · Candida can be seen with Gram-positive staining.
- · Histopathology slides are stained with Gomori methenamine silver staining.
- · Histoplasma is detected by nucleic acid hybridization technique.
ANTIFUNGAL TREATMENT Topical agents
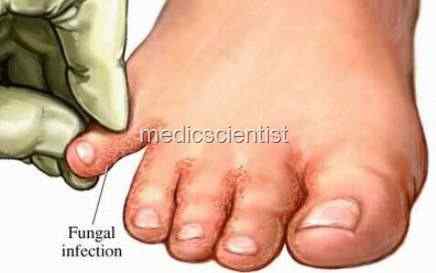 |
| Fungal Infections cutaneous Candida, Tinea versicolor (pityriasis) and ring worm |
Imidazole and Triazoles
- · Cutaneous applications are clotrimazole, ketoconazoleJ miconazole.
- · For cutaneous Candida, Tinea versicolor (pityriasis) and ring worm any of the above may be used.
- .-1- Va inal formulations are miconazole, cIotrimazole.
- · For vaginal candidiasis clotrimazole may be used.
- For ring worm tolnaftate is used.
- Salicylic acid is used for hyperkeratotic lesions of skin.
 |
| Fungal Infections Systemic antifungals |
- Prevention
- Apply powder containing imidazoles or tolnaftate to areas prone to fungal infectionafter bathing.
Topical antifungal
- These preparations may be effective for treatment of dermatophytoses of skin butpreparations not for those of hair or nails .
- Preparation is applied bid to involved area optimally for 4 weeks including at least1 week after lesions have cleared.
- Apply at least 3 cm beyond advancing margin of lesion.These topical agents are comparable.
- Differentiated by cost, base, vehicle, andantifungal activity.
Imidazoles
- Econazole (Spectazole)
- Oxiconizole (Oxistat)
- Sulconizole (Exelderm)
- Sertaconazole (Ertaczo)Clotrimazole (Lotrimin, Mycelex)
- Miconazole (Micatin)
- Ketoconazole (Nizoral)
Allylamines
- Naftifine (Naftin)
- Terbinafine (Lamisil)
Naphthionates
- Tolnaftate (Tinactin)
- Substituted pyridone
- Ciclopirox olamine (Loprox)
Systemic antifungal agents
- For infections of keratinized skin :
- use if lesions are extensive or if infection hasfailed to respond to topical preparations.
- Usually required for treatment of tinea capitis and tinea unguium.
- Also may berequired for inflammatory tineas and hyperkeratotic moccasin-type tinea pedis.
Terbinafine
- 250-mg tablet.
- Allylamine.
- Most effective oral antidermophyte antifungal; lowefficacy against other fungi.
Azole/imidazoles
- Itraconazole and ketoconazole
- Itraconazole 100-mg capsules;
- oral solution (10 mg/mL):Intravenous.
Triazole.
- Needs acid gastricpH for dissolution of capsule.
- Raises levels of digoxin and cyclosporine.
Fluconazole
- 100-, 150-, 200-mg tablets;
- oral suspension (10 or 40 mg/mL);
- 400 mg IV.
Ketoconazole
- 200-mg tablets.
- Needs acid gastric pH for dissolution of tablet.
- Take with food orcola beverage; antacids and H2 blockers reduce absorption.
- The mosthepatotoxic of azole drugs; hepatotoxicity occurs in an estimated one of every10,000–15,000 exposed persons
Griseofulvin Micronized:
- 250- or 500-mg tablets;
- 125 mg/teaspoon suspension.
- Ultramicronized :
- 165- or 330-mg tablets. Active only against dermatophytes;less effective than triazoles.
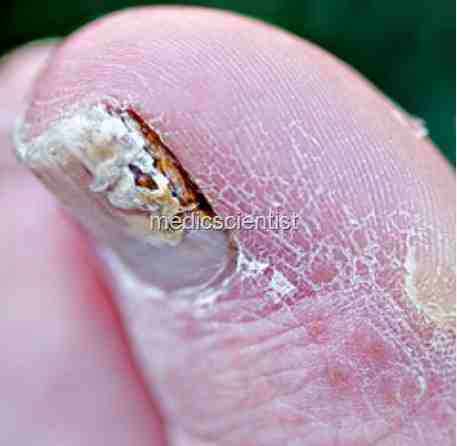
Fungal Infections Systemic antifungals
- Griseofulvin for ring worms.
- Terbinafine 250 mg for onychomycosis (fungal nail infection) and ring worm.
- Treatment is given for 3-6 months.
- The Imidazoles and triazoles may be used for systemic use e.g. fluconazole, itraconazole for blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, aspergillosis.
- Fluconazole penetrates CSF and other body fluids.
- · It is useful in oropharyngeal and oesophageal candidiasis in adults.
- Amphotericin B and fluconazole may be used for cryptococcal meningitis, in AIDS, and coccidiodal meningitis.
