Article Contents ::
Grave’s disease
Grave’s disease is thyrotoxicosis, common in females, associated with high iodine intake, occurring between 20 – 50 years of age.
Grave’s ophthalmopathy
- Besides the signs of thyrotoxicosis, there is Grave’s ophthalmopathy.
- decreased extraocular muscle mobility, and corneal injury, periorbital edema, periorbital and conjunctival inflammation,
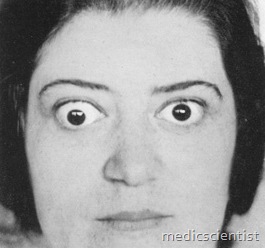
- Ophthalmopathy associated with hyperthyroidism with the clinical characteristics of exophthalmos,
- There are usually bilateral eye signs with sensation of grittiness, eye discomfort, excess tears, proptosis (sclera is visible between the lower border of iris and lower eye lid).
- There may be corneal exposure and damage.
- There is periorbital edema, red sclera and chemosis with diplopia.
- There may be compression of optic nerve leading to papilledema, peripheral field defects, loss of vision.
Treatment of Ophthalmopathy
- No treatment may be required
- Just underlying hyperthyroidism must be treated
- Antithyroid drugs
- Stop smoking
- Artificial tears – 1% methyl cellulose Dark glasses
- Upright sleeping position and diuretics for periorbital edema
- Prednisone 40 – 80 mg daily + cyclosporine Orbital decompression.
- There may be thyroid dermopathy which is skin changes, thickening, and nodules.
- If severe and progressive, surgical decompression of the orbit will be required to treat
- There may be thyroid acropatchy which is like clubbing of fingers.
Lab diagnosis
- TSH level is suppressed and free thyroid Ty T4 are increased.
- There may be microcytic anaemia and thrombocytopenia.
Grave’s disease Treatment
- Antithyroid drugs Radioiodine
- Subtotal thyroidectomy – to reduce the amount of thyroid tissue.
- rapid amelioration of symptoms with a beta-blocker and measures aimed at decreasing thyroid hormone synthesis: the administration of a thionamide, radioiodine ablation, or surgery
- Antithyroid drugs
- Thionamides – Propyl-thiouracil, carbimazole, Methimazole.
- Carbimazole is given 10-20 mg 8 hrly. Propylthiouracil is given 100 mg 8 hrly.
- The doses are reduced when the patient improves. Thyroid function is evaluated 1 month after starting treatment and doses adjusted after 2 months by estimation of T4 levels.
- The side effects of drugs are rashes, urticaria, fever, arthralgia, hepatitis, SLE like syndrome, agranulocytosis.
- Beta blockers ameliorate the symptoms of hyperthyroidism that are caused by increased beta-adrenergic tone
- Propranolol 40 mg 8 hrly may be given to control symptoms.
- For atri’3l fibrillation, Warfarin and Digoxin are used.
