SECONDARY HYPERTENSION
Secondary hypertension is the name given to the hypertension of which the cause is known, and can be corrected in many cases to cure the hypertension.
Renal hypertension :
- This is due to either renal seretion of vasoactive compounds resulting in increased arteriolar tone or volume expansion due to disturance of sodium and fluid balance.
- Uncontrolled hypertension comprises the following entities:
- Secondary hypertension: Elevated blood pressure (BP) that results from an identifiable underlying mechanism Resistant hypertension: failure to achieve goal blood pressure (<140/90 mm Hg for the overall population and <130/80 mm Hg
- for those with chronic kidney disease or diabetes when a patient adheres to maximum tolerated doses of 3 antihypertensive drugs including a diuretic” Other causes: Inadequate treatment, poor patient adherence Poor control is most often due to persistent elevation in systolic BP
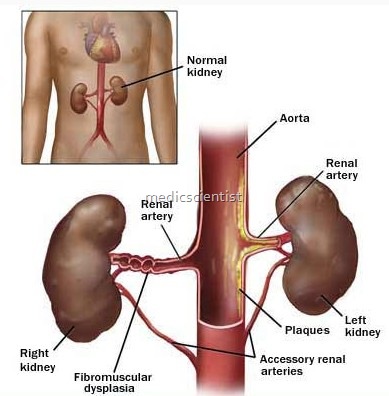
Renal hypertension may be :
- Renovascular hypertension including eclampsia and reeclamsia.
- Renal parenchl’mal hypertension.
- Renal vascular hypertension is due to stenosis of main or a branch of renal artery which activates the -renin angiotensin system (RAS).
- The circulating angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction: LQ.v aldosterone secretion, sodium retention, stimulater: berenglc nervous system a..!Jd al its direct action on:. e arterioles.
- one half of the patients there is elevation of plasma
- In activity RenaL.Parenchymal hypertension is due to in renal parenchymal disease with involvement of mulIe small renal vessels leading to decreased perfusion of renal tissue and bypertensiol
- Peripheral plasma renin activity (PRA) is normal or increased
- Cardiac output normal
- Tilting and Valsalva maneuver have no effect
- Blood volume is increased
- Cardiac output increased
- Tilting & Valsalva maneuver increase blood pressure
- Blood volume is decreased in unilateral disease
Clinical Considerations
- Pseudoresistance:
- In primary care settings, this has been estimated to occur in 40–60% of hypertensive patients.
- Poor adherence
- White-coat effect: Prevalence estimated at 20–30%
- Inaccurate measurement of BP:
- Cuff too small
- Patient not at rest; sitting quietly for 5 minutes
