Unstable Angina Pathophysiology Definition STEMI and NSTEMI
Unstable Angina
- Patients with ischemic heart disease can be divided into two groups:
Patients with stable angina due to chronic coronary artery disease
- Patients with acute coronary syndrome Stable angina pectoris is characterized by chest pain or discomfort radiating to left or both arms, on physical exertion or stress lasting for 5 to 10 minutes and relieved by rest and / or sublingual nitroglycerine.
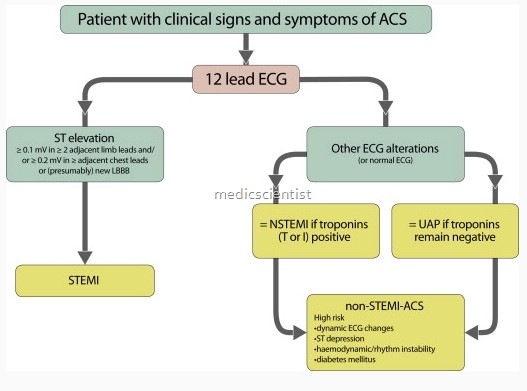
Acute coronary syndrome may be divided into:
- AMI (Acute myocardial infarction) y UA (Unstable angina)
- AMI is STEMI ST-se ment elevation MI
- UA is NSTEMI (Non ST – Segment elevation MI)
- UA pectoris is chest pain or discomfort occurring at rest or mild exertion, lasting more than 10 minutes OR very severe pain of new onset (less than 6 weeks old) OR very severe, prolonged, frequent or crescendoain.
- UA is called NSTEMI when a patient of typical UA has elevated cardiac bio-markers i.e. evidence of myoaralum necrosis (elevated troponins).
Definition
- unstable angina is acute ischemic discomfort without s-t segment elevation and without elevation of serum crdiac markers.
Pathophysiology
- There may be rupture of plaque over a thrombus or atheroma resulting in occlusion of coronary artery. In UA there are white thrombi which are – platelet rich as compared to red thrombi (loose cells) in AMI.
- There may be coronary spasm as in Prinzmetal’s angina (variant angina).
- Rapid development of atherosclerotic obstruction as in restenosis after PCI (percutaneous inervention).
- Acute ischemia secondary to exertion or anaemia.
