Article Contents ::
- 1 Details About Generic Salt :: Felbamat
- 2 Main Medicine Class:: Anticonvulsant
- 3 (FELL-buh-MATE) Felbatol Class: Anticonvulsant
- 4 Drugs Class ::
- 5 Disclaimer ::
- 6 The Information available on this site is for only Informational Purpose , before any use of this information please consult your Doctor .Price of the drugs indicated above may not match to real price due to many possible reasons may , including local taxes etc.. These are only approximate indicative prices of the drug.
Details About Generic Salt :: Felbamat
Main Medicine Class:: Anticonvulsant
(FELL-buh-MATE)
Felbatol
Class: Anticonvulsant
Drugs Class ::
 Action May reduce seizure spread in generalized tonic-clonic or partial seizures and may increase seizure threshold in absence seizures.
Action May reduce seizure spread in generalized tonic-clonic or partial seizures and may increase seizure threshold in absence seizures.
Indications for Drugs ::
 Indications Monotherapy or adjunctive therapy in treatment of partial seizures with and without generalization in epileptic adults. Adjunctive therapy in treatment of partial and generalized seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in children.
Indications Monotherapy or adjunctive therapy in treatment of partial seizures with and without generalization in epileptic adults. Adjunctive therapy in treatment of partial and generalized seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome in children.
Drug Dose ::
 Route/Dosage
Route/Dosage
Because of reports of aplastic anemia, it has been recommended to stop use of this drug unless physician decides that withdrawal would cause greater risk.
Initial Monotherapy
ADULTS & ADOLESCENTS ³ 14 YR: PO 1200 mg/day in 3 or 4 divided doses; increase in 600 mg increments q 2 wk to 2400 mg/day and then 3600 mg/day if indicated.
Conversion to Monotherapy
ADULTS & ADOLESCENTS ³ 14 YR: Initial dose: PO 1200 mg/day in 3 or 4 divided doses, reducing dose of other antiepileptic drugs by 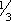 . At wk 2 increase felbamate to 2400 mg/day and at wk 3 increase to 3600 mg/day; continue to reduce dose of other antiepileptic drugs as indicated.
. At wk 2 increase felbamate to 2400 mg/day and at wk 3 increase to 3600 mg/day; continue to reduce dose of other antiepileptic drugs as indicated.
Adjunctive Therapy
ADULTS & ADOLESCENTS ³ 14 YR: Initial dose: PO 1200 mg/day in 3 or 4 divided doses; reduce original dose of other antiepileptic drugs by 20% to 33% for 1 wk. At wk 2 increase felbamate to 2400 mg/day and at wk 3 increase to 3600 mg/day if needed; reduce dosage of other antiepileptic drugs as clinically indicated. CHILDREN 2 to 14 YR WITH LENNOX-GASTAUT SYNDROME: PO15 mg/kg/day in 3 or 4 divided doses while reducing other antiepileptic drugs by ³ 20%. Increase felbamate by 15 mg/kg/day increments at weekly intervals up to 45 mg/kg/day; continue to reduce dosage of other antiepileptic drugs as needed.
Contraindication ::
 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to felbamate or ingredients of this product; hypersensitivity reactions to other carbamates; history of any blood dyscrasia or hepatic dysfunction.
Contraindications Hypersensitivity to felbamate or ingredients of this product; hypersensitivity reactions to other carbamates; history of any blood dyscrasia or hepatic dysfunction.
Drug Precautions ::
 Precautions
Precautions
Pregnancy: Category C. Lactation: Excreted in breast milk. Children: Safety and efficacy not established other than for adjunctive therapy of Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. Elderly patients: Use caution and start with low doses. Clinical experience is limited. Aplastic anemia: It is recommended that use of felbamate be suspended unless health care professional judges that patient’s well-being is at greater risk if drug is discontinued. Carcinogenesis: Drug may have carcinogenic potential. Discontinuation: Withdraw drug slowly to avoid increased seizure frequency. Hypersensitivity: Administer drug with caution to patients with prior hypersensitivity reactions to carbamates. Pre-existing liver failure: Eight cases of acute liver failure have occurred, including 4 deaths, in association with the use of felbamate. Evaluate patients prior to treatment initiation for evidence of pre-existing liver damage; avoid use in patients with pre-existing liver pathology. Once treatment is initiated, monitor ALT, AST, and bilirubin on a weekly basis. The drug should be withdrawn immediately in patients who develop lab findings indicating liver injury. Aplastic anemia: It is recommended that use of felbamate be suspended unless health care professional judges that patient’s well-being is at a greater risk if drug is discontinued.
|
PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS |
|
Drug Side Effects ::
 Adverse Reactions
Adverse Reactions
CNS: Insomnia; headache; anxiety; somnolence; dizziness; nervousness; tremor; abnormal gait; depression; paresthesia; ataxia; dry mouth; stupor; thinking abnormalities; emotional lability. DERM: Acne; rash; pruritus. EENT: Diplopia; abnormal vision; miosis; otitis media; rhinitis; sinusitis; taste perversion; pharyngitis. GI: Dyspepsia; vomiting; constipation; diarrhea; nausea; anorexia; abdominal pain; hiccoughs. GU: Urinary incontinence; intramenstrual bleeding; UTI. HEMA: Aplastic anemia; purpura; leukopenia. HEPA: Increased ALT and AST; acute liver failure. RESP: Upper respiratory tract infection; coughing. OTHER: Fatigue; weight decrease; facial edema; fever; chest pain; pain; hypophosphatemia; myalgia.
Drug Mode of Action ::
 Action May reduce seizure spread in generalized tonic-clonic or partial seizures and may increase seizure threshold in absence seizures.
Action May reduce seizure spread in generalized tonic-clonic or partial seizures and may increase seizure threshold in absence seizures.
Drug Interactions ::
 Interactions
Interactions
Antiepileptic drugs: Felbamate may increase blood levels of phenytoin and valproic acid and decrease blood levels of carbamazepine. Phenytoin or carbamazepine may increase clearance of felbamate.
Drug Assesment ::
 Assessment/Interventions
Assessment/Interventions
- Obtain patient history, including drug history and any known allergies. Note current status and frequency of seizures and use of other antiepileptic drugs, nonprescription drugs, and social drugs (alcohol).
- Assess baseline data on patient’s weight and hematologic and hepatic functions.
- Monitor for effectiveness; note any changes in seizure patterns and frequency.
- If seizures occur, protect patient from injury.
- Weigh patient weekly and record weight.
- Monitor serum levels of felbamate and/or other antiepileptic drugs as necessary.
Drug Storage/Management ::
 Administration/Storage
Administration/Storage
- Instruct patient to take tablet whole with full glass of water; do not crush.
- May administer tablet with food.
- Administer suspension if patient is unable to swallow tablets.
- Shake suspension prior to administration.
- Do not discontinue administration suddenly because of the possibility of increased frequency of seizures.
- Store at room temperature in tightly closed container away from excessive heat, direct sunlight, and moisture.
Drug Notes ::
 Patient/Family Education
Patient/Family Education
- Instruct patient to drink at least 1 full glass of water with each dose.
- Remind patient to take tablet whole; do not crush.
- Inform patient that tablet may be taken with food.
- Caution patient to not stop taking this medication suddenly because of possibility of increasing seizure frequency.
- Advise patient to avoid exposure to sunlight or sunlamps and to use sunscreen or wear protective clothing to avoid photosensitivity reaction.
- Instruct patient and family that if seizures occur, they should protect patient from injury.
- Inform patient to report these symptoms to physician: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, indigestion, constipation, diarrhea, weight loss/gain, anxiety, nervousness, tremors, dizziness, depression, chest pain, fever, headache, poor coordination, drowsiness, sleeplessness, edema (fluid retention), intramenstrual bleeding (women), dry mouth, vision problems and any changes in seizure activity.
- Advise patient that drug may cause drowsiness, dizziness, and vision problems, and to use caution while driving or performing other tasks requiring mental alertness.
