Article Contents ::
- 1 Sleep Disorders
- 2 Average requirement of sleep is 7-8 hours per night.
- 3 Polysomnography
- 4 There are two states of sleep:
- 5 Sleep-wake cycle is affected by
- 6 Narcolepsy
- 7 Sleep apnea
- 8 Somnambulism
- 9 Aruxism
- 10 sleep enuresis
- 11 Sleep disorders are :
- 12 Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) and Cardiovascular disease:
- 13 Clinical features of Sleep Disorders :
- 14 Treatment of Sleep Disorders
Sleep Disorders
- Disturbed sleep is one of the most common health problems.
Average requirement of sleep is 7-8 hours per night.
- States and stages of sleep are defined by characteristic patterns in EEG (electro-encephalogram), EOG (Electrooculogram), EMG (Electromyogram) measured on the chin and neck.
-
Polysomnography
- The continuous recording of electrophysiologic parameters of sleep and wakefulness is termed polysomnography.
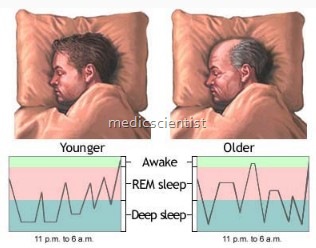
There are two states of sleep:
- Rapid Eye Movement Sleep (REM)
- A Non Rapi Eye Movement Sleep (NREM) There are 4 stages of NREM sleep.
- After onset of sleep there is NREM sleep stages 1 to 4 in one hour. NREM stages 3 and 4 continue for 1/3rd of the night.
- First REM sleep occurs in the 2nd hour of sleep.
Sleep-wake cycle is affected by
- endocrine, thermoregulatory, cardiac, pulmonary, renal, gastrointestinal and neural functions.
- This follows a circadian rhythm.
-
Narcolepsy
- Sudden weakness of muscles, hallucinations and sleep paralysis
-
Sleep apnea
- There is occlusion of airway, or absence of respiratory effort.
-
Somnambulism
- Patients leave the bed and walk about and even do certain activities.
Aruxism
- There is involuntary grinding of teeth.
sleep enuresis
- Bed-wetting.
Sleep disorders are :
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Narcolepsy-Cataplexy syndrome .y Periodic limb movements
- Insomnia.
- The narcolepsy tetrad consists of excessive day time sleepiness, loss of muscle tone without loss of consciousness (cataplexy), hallucinations, sleep paralysis on awakening.
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) and Cardiovascular disease:
- Snoring is a loud sound produced during sleep due to vibration of colla sible art of airwa between posterior c onae and the e i lottis articularl oro..eharyngeal isthumus. Extreme cases of snoring associa ed with apnea and h 0 neas are described as sleep
- Isor er breathin or OSAS.
- OSAS has a high prevalence in the cardiovascular disease patients.
- OSAS affects as many s 30% of coronary artery disease patients, 50% of congestive heart failure patients, 60% of stroke patients, 80% of drug resistant hypertensive patients. OSAS has been associated with’ an almost 5 fold increase in risk of development of cardiovascular disease independent of age, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pres-‘ sure and smoking. ‘
Clinical features of Sleep Disorders :
- Patient is usually obese
- Snoring
- Hypertension
- Hallucinations
- Restless legs syndrome
- Renal failure
- Anaemia and Asthma.
Treatment of Sleep Disorders
- Continuous positive airway pressure Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty by ENT surgeon Weight loss
- Clonazepam and Zolpidem.
