Cardiac Arrhythmias – Supraventricular tachycardia and Ventricular fibrillation —
SVT. A rapid, regular tachycardia in which the pacemaker is found in the sinus node, the atria, or the atrioventricular junction, i.e., above the ventricles
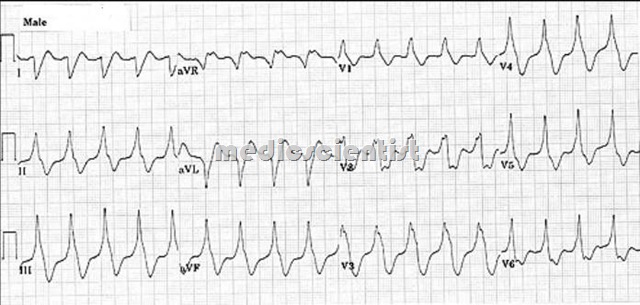
Distinguishing features of SVT with wide QRS from VT —
- Triphasic QRS – rsR or qRs
- . Initial deflection identical to normal beat (RBBB pattern)
- Atrial ectopics precede the acidity
- Alternating BBB patterns
- Identical wide QRS pattern in previous ECG (not showing SVT) which was diagnosed as aberrant.
- These are Life threatening Cardiac Disorders
Slow Ventricular Tachycardia
- is another term used for an accelerated ventricular rhythm. Nonsustained VT is VT of less than 30 seconds.
Trorsades de ointes:
- Polymorphic VPBs with appearance of slow flutter without QRS complexes or T waves is called Torsades de pointes. The ventricular activity revolves around isoelectric line.
Ashman phenomenon:
- Aberration in the intraventricular conduction of an impulse that completes a short cardiac cycle following a long cycle because the long cycle results in delay of repolarization.
Concordance :
- Abnormal wide QRS complexes all in one direction in all 6 precordial leadsis called concordance of QRS.
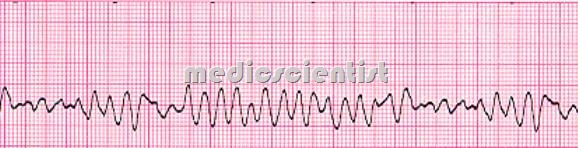
Ventricular fibrillation —
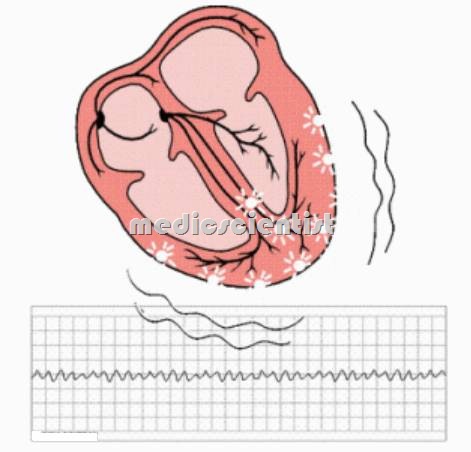
- A treatable, but lethal dysrhythmia present in nearly half of all cases of cardiac arrest. It is marked on the electrocardiogram by rapid, chaotic nonrepetitive waveforms; and clinically by the absence of effective circulation of blood (pulselessness)
Causes of VF Ventricular fibrillation
- · IHD (Ischemic heart disease)
- · Antiarrhythmic drugs which prolong QT
- · Torsade de pointes
- · Severe hypoxia
- · WPW with AF with rapid ventricular response
- · Electric shock and Congenital long QT
- · HOCM (Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy)
- · Arryhthmogenic RV dysplasia
- · Brugada syndrome.
- VF is recognized by grossly irregular undulations of varying amplitude, contour, and rate.
Treatment of Ventricular fibrillation
- Drugs – Same as for VT.
- Defibrillation – Asynchronized DC shock – 200 to 400 Joules.
- External electric cardioversion is performed by placing two paddles to the right of sternum at level of second rib and left anterior aXillary line in the fifth intercostal space.
- (Qiazepam is given in the conscious patient)
