Article Contents ::
Tubulointerstitial Diseases of the Kidney
- Primary tubulointerstitial diseases of the kidneyare characterized by abnormalities of structure and function of tubules and the interstitium.
- The glomeruli and renal vasculature are involved to a Jesser extent.
- The biopsy specimens and the urine sediments do not help in diagnosis.
- Acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) is most often induced by drug therapy
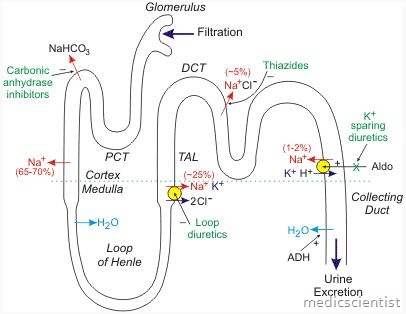
In proximal tubule dysfunction
- there is hypokalemia, glycosuria, phosphaturia, uricosuria,
- bicarbonaturia, aminoaciduria, like in proximal or type 11 renal tubular acidosis (RTA).
- The proteinuria is usually less than 2 gjday.
- These findings are called the Fanconi syndrome.
- There is hyperch/oremic metabolic acidosis and urine pH is less than 5.3.
- There is a reduce,d excretion of ammonia.
- There may be no turia and polyuria as in analgesic nephropathy and sickle cell disease.
Causes of acute interstitial nephritis
- Acute interstitial nephritis may be caused by beta lactam antibiotics, sulphonamides, quinoiones, vancomycin, erythromycin, rifampicin, ethambutol, acyclovir.
- Non steroidal antiinflmmatory drugs.
- Diuretics – thiazides, frusemide, triamterene.
- Anticonvulsants – Phenytoin, phenobarbitol, carbamazepine.
- Captopril, Omeprazoie, Allopurinol.
- Infections (bacteria) – Streptococcus, staphylococcus, salmonella, brucella.
- Viruses – Epstein Barr virus, Cytomegalovirus,
- HIV.
- Leptospira, Rickettsia, Mycoplasma.
- Sarcoidosis.
- Antitubule basement membrane disease.
Causes of chronic tubulo interstitial diseases
- 1. Polycystic kidney
- 2. Medullary sponge kidney
- 3. Analgesic nephropathy
- 4. Lead nephropathy
- 5. Hyperuricemia
- 6. Hypercalcemia
- 7. Hypokalemia
- 8. Fabry’s disease
- 9.. Sjogren’s syndrome
- 10. Leukemia
- 11. Multiple myeloma
- 12. Sickle cell disease
- 13. Chronic pyelonephritis
- 14. Radiation nephritis.
Treatment of Tubulointerstitial Diseases
- Treatment is management ofthe presenting feertures, withdrawal of the offending drug or agent, treatment of the etiology, dialysis, and renal transplant.
