Amoebiasis Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatments and Causes Entamoeba histolytica
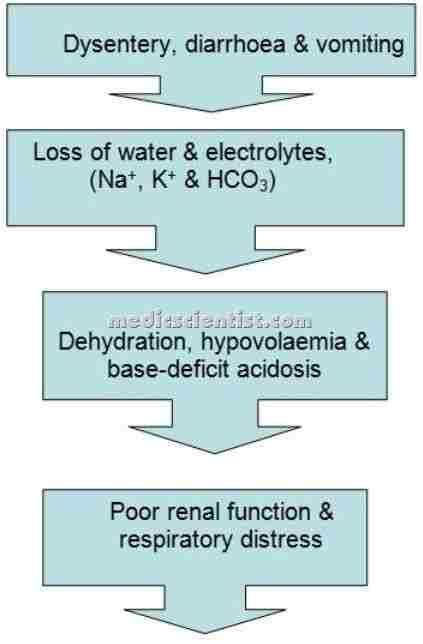
Approx. 500 million people in tropical countries are infected. Infection or colonization with amebas, esp. Entamoeba histolytica.The infection typically begins in the colon but may spread to other organs, such as the liver or, less often, the skin or lungs
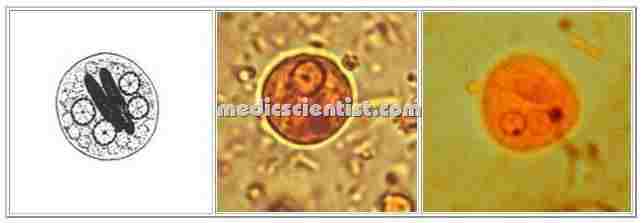 |
| Amoebiasis infection Diagnosis Treatment protozoan Entamoeba histolytica |
Amoebiasis
- Amoebiasis is infection with intestinal protozoan called Entamoeba histolytica.
- Usually the infections are asymptomatic.
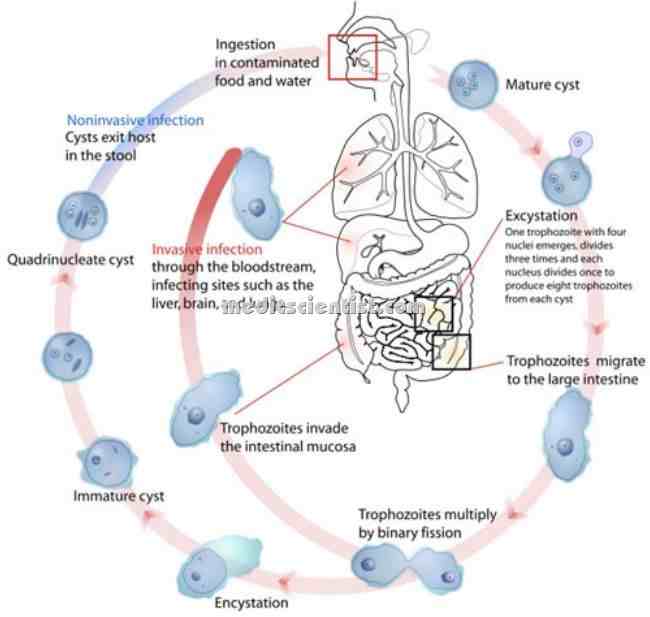 |
| Amoebiasis infection life cycle |
LIFE CYCLE
- E. hystolytica enters the body of man from water, food, hands, by fecal contamination.
- Motile trophozoites are released from cysts in small intestine and may remain in large bowel as harmless commensals.
- The cysts are shed in stools. Trophozoites may invade the blood stream, and go to liver, lungs and brain resulting in amoebic abscess.
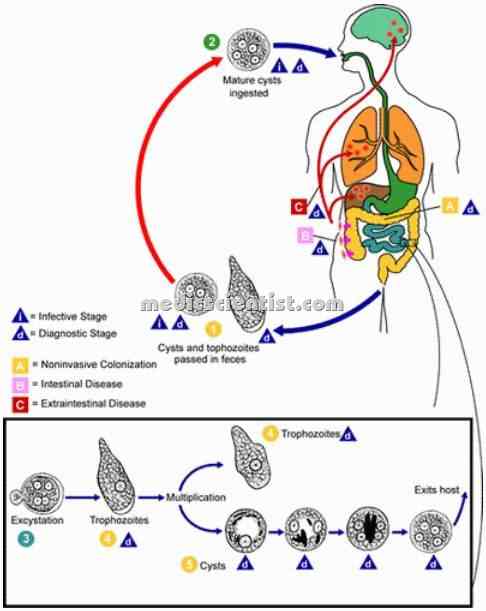 |
| Amoebiasis infection Diagnosis Treatment protozoan Entamoeba histolytica life cycle |
CLINICAL FEATURES Intestinal amoebiasis
- · May be asymptomatic.
- · Abdominal pain, diarrhea, malaise, weight loss are seen.
- · May involve cecum and mimic appendicitis.
- · Patient may have dysentery with 10 – 12 stools/ day containing blood and mucus.
- Most infected patients have no tissue invasion and, thus, are asymptomatic.
- Acute colitis, when it occurs, is marked by bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, tenesmus, and weakness.
- The dysentery lasts 3 to 4 weeks
- The symptoms may be confused with those of ulcerative colitis.
- · There may even be severe pain, profuse diarrhea, high fever.
- · Fever may not be present.
- · Ameboma may develop which is a mass in the
- abdomen due to amoebic infection.
- ·Stools are heme-positive.
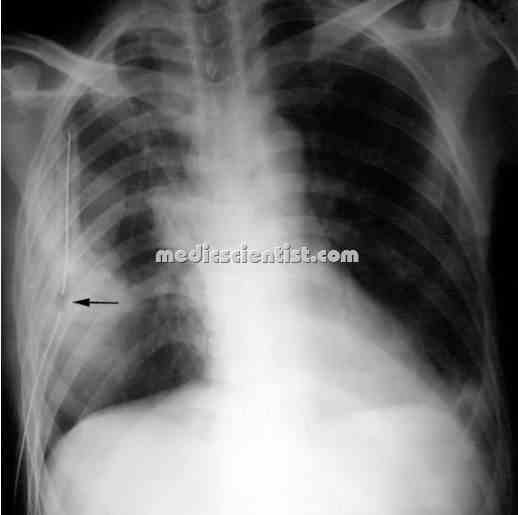 |
| Amoebic liver abscess |
Amoebic liver abscess:
- · Usually occurs in young patients, acutely, with fever, and pain, in right upper quadrant of abdomen. There may be tenderness.
- ·Jaundice, and diarrheas are rare.
Complications of Liver abscess:
- · There may be pleuropulmonary involvement by spread from the liver or rupture into pleural cavity.
- · Abscess may also rupture into peritoneum.
- · Left lobe amoebic abscess of liver may rupture
- into pericardium and may be fatal.
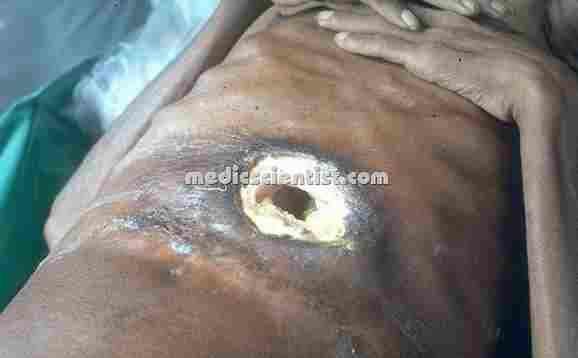 |
| Extra intestinal amoebiasis |
Extra intestinal amoebiasis:
- · Genitourinary tract involvement
- · Genital ulcers and Cerebral involvement.
 |
| Amoebiasis infection Diagnosis |
DIAGNOSIS
- · Barium study – not done nowadays.
- · Ultrasound, CT, MRI, X-ray.
- · All these can detect oval or round cysts which are hypoechoic.
- · Stool examination – reveals positive test for heme, amoebic cysts, trophozoites.
- At least three fresh stool specimens should be examined.
- · Sigmoidoscopy – for chronic cases only.
- · Serology – ELISA.
- · Leucocytosis and Anaemia.
TREATMENT Intestinal amoebiasis
- Nitroimidazole compounds – Metronidazole-oral 750 mg three times daily for 5-10 days.
- Side effects are nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort, metallic taste.
- Other Imidazoles are Tinidazole and Ornidazole.
- All patients should also be given luminal agents to eradicate cysts – Oiloxanide furoate 500 mg three times a day for 10 days,
- or Iodoquinol 650 mg TIO for 20 days or Paromomycin 500 mg TIO for 10 days.
TREATMENT Amoebic liver abscess:
- Metronidazole 750 mg orally or IV TIO for 5-10 days or Tinidazole 2 g orally or 800 mg TID for 5 days or Ornidazole 2 gm orally.
- Oiloxanide furoate 500 mg TDS is given for cysts. Amoebic liver abscess must be aspirated if there is secondary infection, or if it does not respond in three days, as it may rupture. The aspirated pus is typically described as anchovy sauce pus.
FREE-LIVING AMOEBAS Naegleria infections
- May cause meningoencephalitis with seizures, coma and death.
Treatment –
- Amphotericin Band
- Rifampin Acanthamoeba
- This causes encephalitis in chronically ill patients like patients of AIDS. It is usually fatal.
| Patient Care: |
|
