Article Contents ::
Herpes Zoster Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis for Herpes Zoster ::
- Isolation of VZV in tissue culture, detection of VZV DNA by PCR, or direct immunofluorescent staining of cells from the lesion base
- Seroconversion or a fourfold or greater rise in antibody titer between convalescent- and acute-phase serum specimens. The fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen (FAMA) test, immune adherence hemagglutination test, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) are the most frequently used techniques.
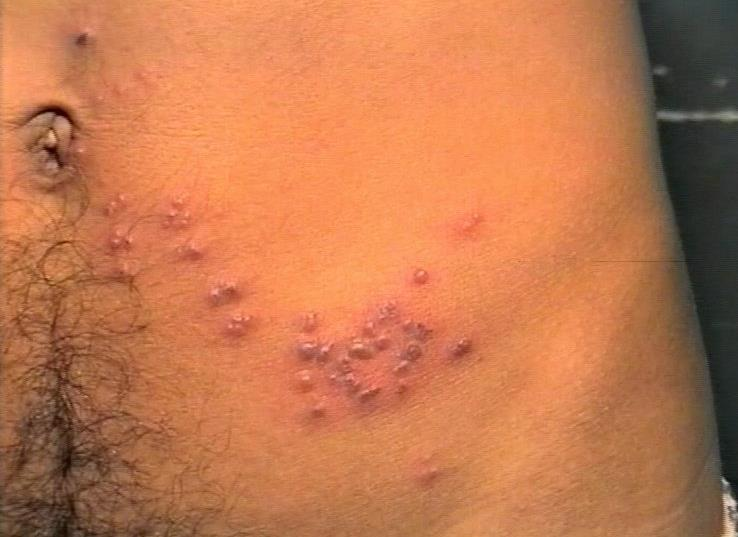
- Note the fluid filled vesicles, on one side of the body, affecting one dermatome. The distribution is diagnostic of Herpes Zoster (Shingles). Redness around the vesicles denotes active stage.
- Eruption of grouped vesicles on an erythematous base usually limited to a single dermatome (“shingles”); disseminated lesions can also occur, especially in immunocompromised pts. Tzanck preparation reveals multinucleate giant cells; indistinguishable from herpes simplex except by culture. Postherpetic neuralgia, lasting months to years, may occur, especially in the elderly
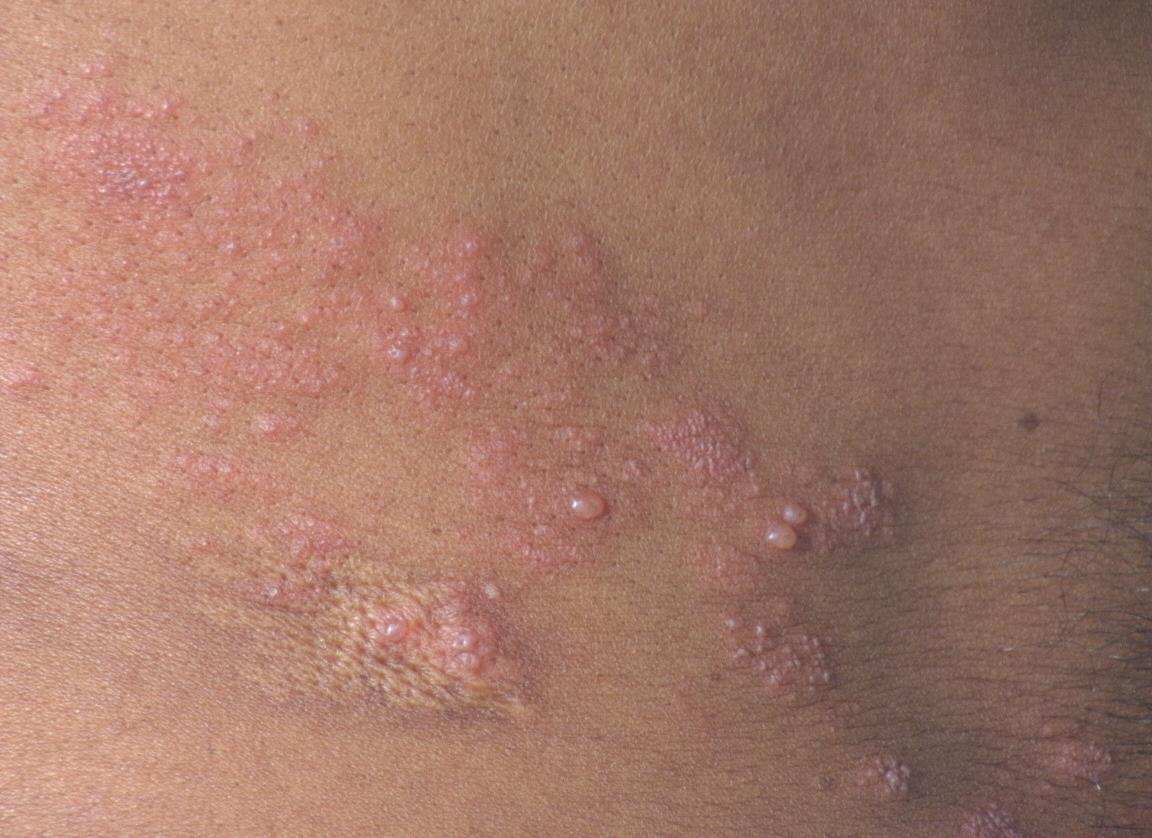
- Very early eruption is seen over at the back end
- • Zoster of the facial nerve presents with lesions in the external auditory canal (Ramsay Hunt syndrome)
• Disseminated zoster may present with widespread cutaneous and visceral lesions
• Extensive and haemorrhagic vesicles may develop in patients with AIDS - the redness of skin which appears first. Then tiny vesicles form, and gradually enlarge filled with a clear fluid.The second picture shows a later stage , where vesicles are drying and scabs are formed
- Trigeminal zoster may affect:: the ophthalmic nerve (causing severe conjunctivitis)
- the maxillary nerve (causing vesicles on the uvula or tonsils)
- the mandibular nerve (causing vesicles on the floor of the mouth and on the tongue
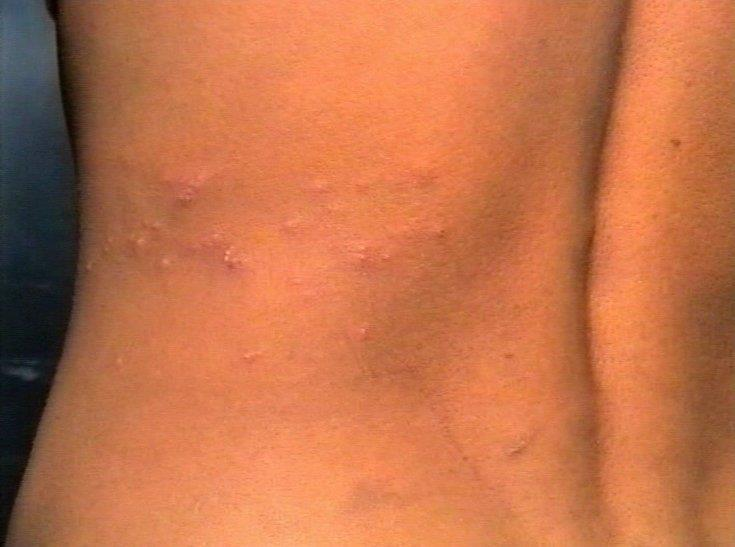
- Observe the blebs and vescicles over the left side of the abdomen and back, which stop at the midline, at both ends.
- Painful, Vescicular rash stopping in midline is the classic picture of Herpes zoster, which affects a single dermatome.
- The redness around the blebs, and fluid filled blebs, means that it is acute erupting rash. So anti-viral drugs should be given.
- Later scabs will form,and then fall off
Treatment for Herpes Zoster
- Antiviral therapy: Acyclovir for children <12 years of age (20 mg/kg q6h, if initiated early in disease) and for adolescents and adults (800 mg five times daily for 5–7 days for chickenpox of le24 h duration) is recommended. Valacyclovir and famciclovir are probably as efficacious or more so.
- Good hygiene, meticulous skin care, and antipruritic drugs are important to relieve symptoms and prevent bacterial superinfection of skin lesions.
- Zoster: Lesions heal more quickly with antiviral treatment: acyclovir, 800 mg five times daily for 7–10 days; famciclovir, 500 mg tid for 7 days (one study also showed twofold faster resolution of PHN with this agent); or valacyclovir, 1 g tid for 5–7 days.
